Ο πιο επικίνδυνος αστεροειδής που γνώρισε η ανθρωπότητα πέρυσι δεν θα χτυπήσει τη Γη για τουλάχιστον 100 χρόνια

Ο αστεροειδής «2021 QM1» αφαιρέθηκε επίσημα από τη λίστα επικινδυνότητας αστεροειδών του Ευρωπαϊκού Οργανισμού Διαστήματος. Απομένουν άλλοι 1.377 αστεροειδείς. (Η εντύπωση του καλλιτέχνη για έναν αστεροειδή που ορμάει προς τη Γη.)
Ο αντίκτυπος αποκλείεται το 2052 καθώς ο Ευρωπαϊκός Οργανισμός Διαστήματος (ESA) ξεκινά την αντίστροφη μέτρηση για την Ημέρα Αστεροειδών
Ακριβώς στην ώρα για την Παγκόσμια Ημέρα Αστεροειδών: ένας απειλούμενος διαστημικός βράχος που βρίσκεται στην κορυφή των λιστών κινδύνου σε όλο τον κόσμο για μήνες, με πραγματική πιθανότητα να χτυπήσει τη Γη στις 2 Απριλίου 2052. Τώρα, η ομάδα αστεροειδών της Ευρωπαϊκής Διαστημικής Υπηρεσίας εργάζεται με ειδικούς στο Παρατηρητήριο της Νότιας Ευρώπης ([{” attribute=””>ESO) has officially removed ‘2021 QM1’ from their asteroid risk list, a result of skilled observations and analysis of the faintest asteroid ever observed with one of the most sensitive telescopes ever constructed.
With Asteroid Day Live 2022 set for June 30, we can safely say that the riskiest asteroid known to humankind in the last year will not impact the Earth – at least not for the next century.
What was it like to track this asteroid? Get the full story in ESA’s fascinating behind-the-scenes look at how European experts handle asteroid risks in the official countdown to Asteroid Day live on June 30, airing at 10:25 CEST on AsteroidDay.org and via ESA WebTV.

Asteroid 2021 QM1, once thought to have a chance of impacting Earth in 2052, was spotted passing through a region of the sky with the Milky Way just behind it. The small, faint, receding asteroid had to be found against a backdrop of thousands of stars, with red crosses indicating the path of the object. Credit: ESO/O. Hainaut
Impact 2052
2021 QM1 was first discovered on August 28, 2021, by the Mount Lemmon Observatory, located north of Tucson, Arizona. At the beginning, nothing stood out as unusual about the discovery – about a dozen new near-Earth asteroids are identified every dark night. Routine follow-up observations were subsequently acquired from telescopes around the globe, but these began to tell a more worrying story.
“These early observations gave us more information about the asteroid’s path, which we then projected into the future,” said Richard Moissl, ESA’s Head of Planetary Defense.
“We could see its future paths around the Sun, and in 2052 it could come dangerously close to Earth. The more the asteroid was observed, the greater that risk became.”
Είναι σημαντικό να σημειωθεί ότι οι υπολογισμοί τροχιάς που βασίζονται σε μόνο λίγες νύχτες παρατηρήσεων υπόκεινται σε κάποια αβεβαιότητα, γι’ αυτό οι αστεροειδείς προστίθενται συχνά στη λίστα κινδύνου της ESA αμέσως μετά την ανακάλυψή τους και στη συνέχεια αφαιρούνται μόλις συλλεχθούν περισσότερα δεδομένα και αβεβαιότητες μειώνουν τη βεβαιότητα. , και ο αστεροειδής αποδείχθηκε ασφαλής. Με αυτή την ευκαιρία, αυτό δεν κατέστη δυνατό.
Η ατυχής κοσμική ευθυγράμμιση
Καθώς ο κίνδυνος φαινόταν να αυξάνεται, συνέβη μια τέλεια κοσμική ευθυγράμμιση: η διαδρομή του αστεροειδούς τον έφερε πιο κοντά στον Ήλιο όπως φαίνεται από τη Γη, καθιστώντας αδύνατο να φανεί για αρκετούς μήνες από τη φωτεινή λάμψη του άστρου μας.
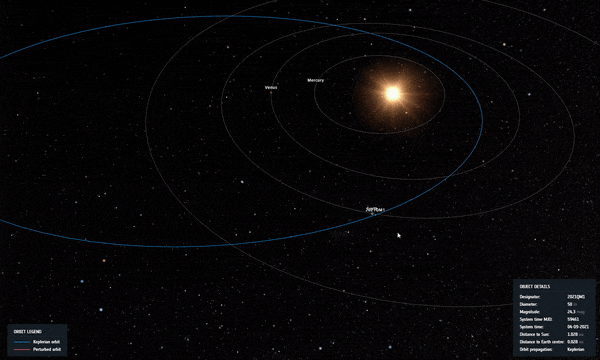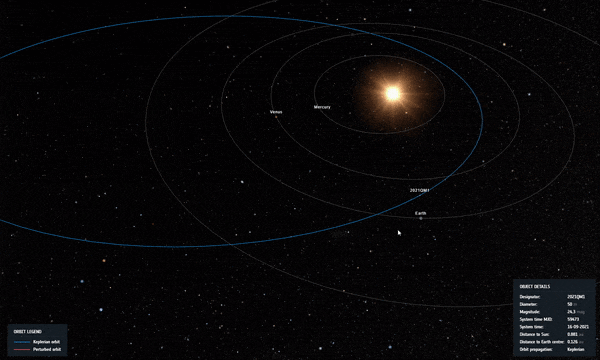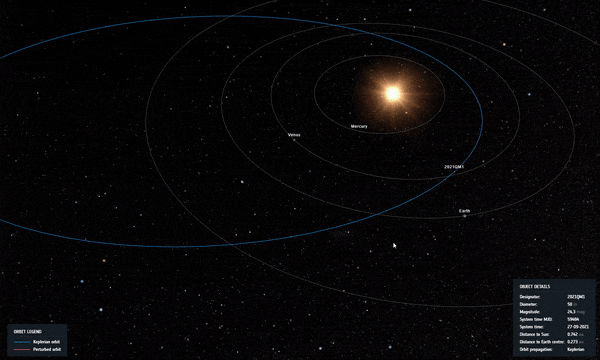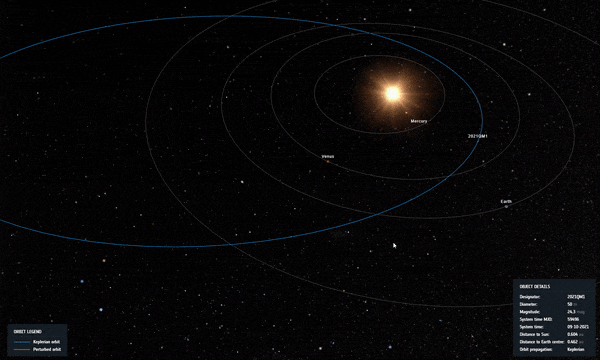
Σε τροχιά 2021 QM1 καθώς περνά κοντά στον Ήλιο στον ουρανό όπως φαίνεται από τη Γη, λίγο μετά την ανακάλυψή του. Πίστωση: ESA
«Έπρεπε απλώς να περιμένουμε», εξήγησε ο Μάρκο Μικέλι, αστρονόμος στο Κέντρο Συντονισμού Αντικειμένων Κοντά στη Γη (NEOCC) της Ευρωπαϊκής Διαστημικής Υπηρεσίας.
“Αλλά για να σταματήσουμε τα πράγματα, μάθαμε ότι το 2021 QM1 απομακρύνονταν επίσης από τη Γη στην τρέχουσα τροχιά του – πράγμα που σημαίνει ότι μέχρι να φύγει από την λάμψη του ήλιου, μπορεί να ήταν πολύ αχνό για να ανιχνευθεί.”
Όσο περίμεναν, ετοιμάστηκαν.
Πρόσβαση κατά προτεραιότητα σε ένα από τα πιο ισχυρά τηλεσκόπια στη Γη
Ευρωπαϊκό Νότιο Παρατηρητήριο Πολύ μεγάλο τηλεσκόπιο (VLT) Ήταν έτοιμο και έτοιμο. Μόλις ο αστεροειδής ύψους 50 μέτρων απομακρυνθεί από το φως του ήλιου – και οι καιρικές συνθήκες το επιτρέπουν – το VLT της ESO θα εστιάσει τον καθρέφτη 8 μέτρων του στους βράχους που εξαφανίζονται.

Δραματική δύση του φεγγαριού πίσω από το Πολύ Μεγάλο Τηλεσκόπιο (VLT) της ESO, Χιλή. Καθώς το φεγγάρι δύει, ο ήλιος πρόκειται να ανατείλει στον αντίθετο ορίζοντα. Το Very Large Telescope (VLT) έχει ήδη κλείσει τα μάτια του μετά από μια μακρά νύχτα παρατηρήσεων, οι χειριστές τηλεσκοπίων και οι αστρονόμοι κοιμούνται ενώ οι τεχνικοί της ημέρας, οι μηχανικοί και οι αστρονόμοι ξυπνούν για μια νέα εργάσιμη ημέρα. Οι επιχειρήσεις δεν σταματούν ποτέ στο πιο παραγωγικό Αστρονομικό Παρατηρητήριο του κόσμου. Πίστωση: G.Gillet / ESO
«Είχαμε ένα σύντομο παράθυρο για να ανακαλύψουμε τον επικίνδυνο αστεροειδή μας», εξήγησε ο Olivier Hainaut, αστρονόμος στο ESO.
«Για να κάνει τα πράγματα χειρότερα, περνούσε από μια περιοχή του ουρανού με[{” attribute=””>Milky Way just behind. Our small, faint, receding asteroid would have to be found against a backdrop of thousands of stars. These would turn out to be some of the trickiest asteroid observations we have ever made”.
Faintest asteroid ever observed
Over the night of May 24, ESO’s VLT took a series of new images. The data arrived and Olivier and Marco began to process them, stacking subsequent observations on top of each other and removing the background stars: it took some time.

ESO’s Very Large Telescope captures 2021 QM1 which for months topped risk lists around the globe. This pivotal sighting ruled out Earth impact in the year 2052. Over the night of May 24, the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope took a series of images of an asteroid that had topped risk lists around the globe for months. These images were some of the trickiest asteroid experts had taken, as the faint asteroid 2021 QM1 receded from view against a very starry backdrop. A series of images were processed, stacked on top of each other and stars were removed, revealing the faintest asteroid observed. Credit: ESA
The result? A positive detection of the faintest asteroid ever observed. With a magnitude of 27 on the scale used by astronomers to describe the brightness of objects in the sky, 2021 QM1 was 250 million times fainter than the faintest stars visible to the naked eye from a dark spot. (In this astronomical scale of visible magnitudes, the brighter an object appears the lower the value of its magnitude, while the brightest objects reach negative values, e.g. the Sun is magnitude -27).
Olivier was certain this small blur was in fact an asteroid, and Marco was certain that given its location, it was our asteroid.
Safe at last?
With these new observations, our risky asteroid’s path was refined, ruling out an impact in 2052, and 2021 QM1 was removed from ESA’s risk list. Another 1,377 remain.

The position of each asteroid at 12:00 CEST on June 13, 2022, is plotted. Each asteroid is a segment representing its motion over 10 days. Inner bodies move faster around the Sun (yellow circle at the center). Blue represents the inner part of the Solar System, where the Near Earth Asteroids, Mars crossers, and terrestrial planets are. The Main Belt, between Mars and Jupiter, is green. The two orange ‘clouds’ correspond to the Trojan asteroids of Jupiter. Credit: © ESA/Gaia/DPAC; CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO, Acknowledgments: P. Tanga (Observatoire de la Côte d’Azur)
More than one million asteroids have been discovered in the Solar System, almost 30 000 of which pass near Earth, with many more expected to be out there. ESA’s Planetary Defence Office, NEOCC and astronomers around the globe are looking up to keep us safe, working together to ensure we know well in advance if an asteroid is discovered on a collision course.
Watch Asteroid Day Live
How worried are the world’s asteroid experts? How did it feel to track humankind’s most risky asteroid? Get the full story in ESA’s 30-minute program counting down to Asteroid Day live on June 30, airing at 10:25 CEST on AsteroidDay.org and on ESA WebTV.

Fallen trees at Tunguska, Imperial Russia, seen in 1929, 15 km from epicenter of the aerial blast site, caused by the explosion of a meteor in 1908. Credit: Photo N. A. Setrukov, 1928
Asteroid Day is the United Nations-sanctioned day of public awareness of the risks of asteroid impacts, held annually on June 30. This year sees its return to Luxembourg for an in-person event following two years of living entirely in the virtual realm. Asteroid experts from ESA, from across Europe and worldwide will converge on the city to take part in a packed four-hour live program of panels and one-on-one interviews.

“Ερασιτέχνης διοργανωτής. Εξαιρετικά ταπεινός web maven. Ειδικός κοινωνικών μέσων Wannabe. Δημιουργός. Thinker.”
