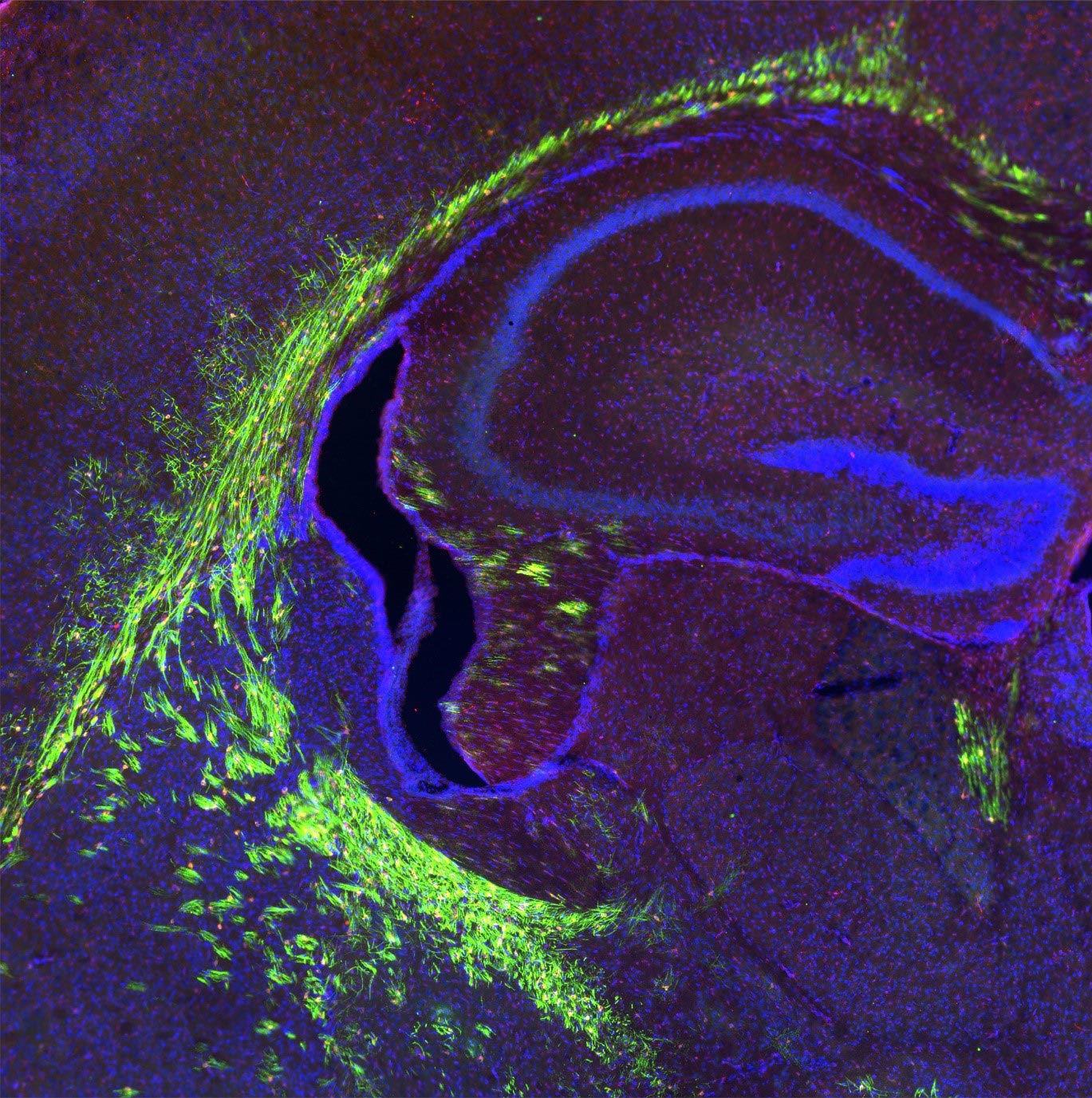
Εγκέφαλος του αναπτυσσόμενου προκλινικού μοντέλου με μυελινωμένους άξονες (φαίνεται με πράσινο). Επιστήμονες από τη Σιγκαπούρη ανακάλυψαν τον κρίσιμο ρόλο της μεταφορικής πρωτεΐνης Mfsd2a στη ρύθμιση των εγκεφαλικών κυττάρων που διατηρούν τα έλυτρα μυελίνης, τη μονωτική μεμβράνη που περιβάλλει τα νεύρα. Αυτά τα αποτελέσματα δημοσιεύτηκαν στο Journal of Clinical InvestigationΜπορεί να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των επιπτώσεων της γήρανσης στον εγκέφαλο. Το Mfsd2a μεταφέρει τη λυσοφωσφατιδυλοχολίνη (LPC), ένα λιπίδιο που περιέχει ωμέγα-3 λιπαρά οξέα, στον εγκέφαλο για μυελογένεση. Πιστοποίηση: Δρ. Vetrivel Sengotuvil
Οι ερευνητές ανακάλυψαν ότι η πρωτεΐνη μεταφορέας Mfsd2a είναι απαραίτητη για τη ρύθμιση των εγκεφαλικών κυττάρων που διατηρούν τα περιβλήματα μυελίνης που προστατεύουν τα νεύρα. Αυτή η ανακάλυψη θα μπορούσε να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των επιπτώσεων της γήρανσης στον εγκέφαλο και να οδηγήσει σε θεραπείες για νευρολογικές διαταραχές που προκαλούνται από μειωμένη μυελίωση.
Επιστήμονες από τη Σιγκαπούρη έδειξαν τον κρίσιμο ρόλο που παίζει μια ειδική πρωτεΐνη μεταφορέας στη ρύθμιση των εγκεφαλικών κυττάρων που διασφαλίζουν ότι τα νεύρα προστατεύονται από καλύμματα που ονομάζονται έλυτρα μυελίνης. Τα ευρήματα, δημοσιεύθηκαν από ερευνητές της Ιατρικής Σχολής Duke-NUS και του Εθνικού Πανεπιστημίου της Σιγκαπούρης Journal of Clinical InvestigationΜπορεί να βοηθήσει στη μείωση των βλαβερών επιπτώσεων της γήρανσης στον εγκέφαλο.
Μια μονωτική μεμβράνη που περιβάλλει τα νεύρα, τα έλυτρα μυελίνης διευκολύνουν την ταχεία και αποτελεσματική αγωγή των ηλεκτρικών σημάτων σε όλο το νευρικό σύστημα του σώματος. Όταν το περίβλημα της μυελίνης είναι κατεστραμμένο, τα νεύρα μπορεί να χάσουν την ικανότητά τους να λειτουργούν και να προκαλέσουν νευρολογικές διαταραχές. Με την ηλικία, τα έλυτρα μυελίνης μπορεί φυσικά να αρχίσουν να φθείρονται, γι’ αυτό και οι ηλικιωμένοι χάνουν τις σωματικές και πνευματικές τους ικανότητες.
Η απώλεια των περιβλημάτων μυελίνης συμβαίνει κατά τη διάρκεια της φυσιολογικής διαδικασίας γήρανσης και σε νευροεκφυλιστικές ασθένειες, όπως η σκλήρυνση κατά πλάκας και[{” attribute=””>Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Sengottuvel Vetrivel, Senior Research Fellow with Duke-NUS’ Cardiovascular & Metabolic Disorders (CVMD) Program and lead investigator of the study. “Developing therapies to improve myelination—the formation of the myelin sheath—in aging and disease is of great importance to ease any difficulties caused by declining myelination.”
To pave the way for developing such therapies, the researchers sought to understand the role of Mfsd2a, a protein that transports lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)—a lipid that contains an omega-3 fatty acid—into the brain as part of the myelination process. From what is known, genetic defects in the Mfsd2a gene leads to significantly reduced myelination and a birth defect called microcephaly, which causes the baby’s head to be much smaller than it should be.

Dr. Sengottuvel Vetrivel (left) and Prof David Silver (right). Credit: Duke-NUS Medical School
In preclinical models, the team showed that removing Mfsd2a from precursor cells that mature into myelin-producing cells—known as oligodendrocytes—in the brain led to deficient myelination after birth. Further investigations, including single-cell RNA sequencing, demonstrated that Mfsd2a’s absence caused the pool of fatty acid molecules—particularly omega-3 fats—to be reduced in the precursor cells, preventing these cells from maturing into oligodendrocytes that produce myelin.
“Our study indicates that LPC omega-3 lipids act as factors within the brain to direct oligodendrocyte development, a process that is critical for brain myelination,” explained Professor David Silver, the senior author of the study and Deputy Director of the CVMD Program. “This opens up potential avenues to develop therapies and dietary supplements based on LPC omega-3 lipids that might help retain myelin in the aging brain—and possibly to treat patients with neurological disorders stemming from reduced myelination.”
Previously, Prof Silver and his lab discovered Mfsd2a and worked closely with other teams to determine the function of LPC lipids in the brain and other organs. The current research provides further insights into the importance of lipid transport for oligodendrocyte precursor cell development.
“We’re now aiming to conduct preclinical studies to determine if dietary LPC omega-3 can help to re-myelinate damaged axons in the brain,” added Prof Silver. “Our hope is that supplements containing these fats can help to maintain—or even improve—brain myelination and cognitive function during aging.”
“Prof Silver has been relentless in investigating the far-reaching role of Msdf2a ever since he discovered this important lipid transport protein, alluding to the many possible ways of treating not only the aging brain but also other organs in which the protein plays a role,” said Professor Patrick Casey, Senior-Vice Dean for Research. “It’s exciting to watch Prof Silver and his team shape our understanding of the roles that these specialized lipids play through their many discoveries.”
Reference: “Deficiency in the omega-3 lysolipid transporter Mfsd2a leads to aberrant oligodendrocyte lineage development and hypomyelination” by Vetrivel Sengottuvel, Monalisa Hota, Jeongah Oh, Dwight L. Galam, Bernice H. Wong, Markus R. Wenk, Sujoy Ghosh, Federico Torta and David L. Silver, 27 April 2023, The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
DOI: 10.1172/JCI164118

“Ερασιτέχνης διοργανωτής. Εξαιρετικά ταπεινός web maven. Ειδικός κοινωνικών μέσων Wannabe. Δημιουργός. Thinker.”